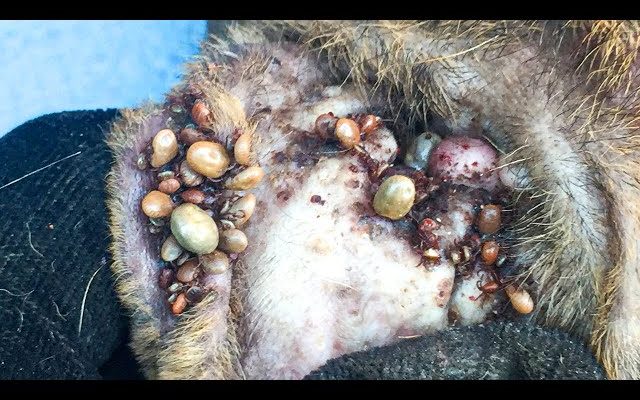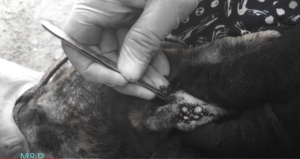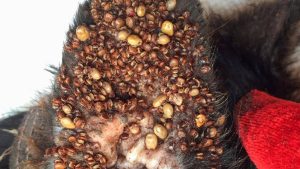
Mango worms are a type of parasitic larvae that can infect dogs. These worms are the larvae of the mango fly, also known as the tumbu fly. The mango fly is native to Africa, but it has spread to other parts of the world, including South America and Asia.
When a mango fly lays its eggs on a dog’s skin, the larvae hatch and burrow into the dog’s skin. The larvae then grow and feed on the dog’s tissue, causing painful and sometimes life-threatening infections. Mango worms are most commonly found in warm, humid areas, and they are more common in dogs that spend a lot of time outside.

To prevent mango worm infections, it is important to regularly check your dog’s skin and body for any lumps or bumps. Shampooing and grooming your dog can also help to prevent infections and to feel their skin for tell-tale signs of symptoms of parasites. If you suspect that your dog has a mango worm infection, it is important to seek veterinary care as soon as possible.
So, What Are Mangoworms In Dogs?
Mangoworms are a type of parasitic worm that live in the skin of dogs. They are also known as Cordylobia Anthropophaga, and are commonly found in dogs in tropical and subtropical regions. The larvae of the worm burrow into the skin of the dog and create a small hole, which they use to feed and grow.


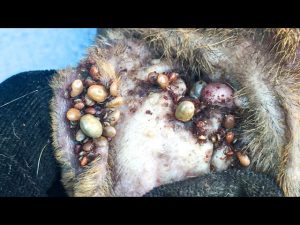
The adult worm is approximately 1.5 cm in length and is reddish-brown in color. The larvae are smaller, measuring about 0.5 cm in length. The larvae can be seen as small black dots on the skin of the dog, and are often mistaken for ticks or other small insects.
Mangoworms are primarily found in rural areas, where dogs have access to open spaces and are not regularly treated for parasites. They are also more common in dogs that have thick fur, as the larvae can easily burrow into the skin and hide from view.
If left untreated, mangoworms can cause significant damage to the skin of the dog. The larvae can grow up to 2 cm in length and can cause abscesses, inflammation, and infection. In severe cases, the larvae can even cause damage to internal organs.
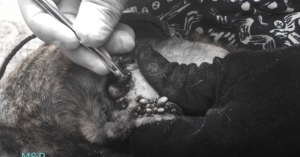
Mango worms can be easily treated by a veterinarian who will remove the worms and clean the affected area. In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent infection.
It is important to note that mango worms are not the only parasites that can affect dogs. Other parasites, such as heartworm and fleas, can also cause health problems for dogs. It is important to regularly check your dog for signs of infestation and seek veterinary care if necessary.
Life Cycle of Mango Flies
Mango flies, also known as tumbu flies, are a type of parasitic fly that lays its eggs on the soil or on objects that come into contact with the host animal. These flies are commonly found in sub-Saharan Africa and are known to infest domestic animals, including dogs.
The life cycle of mango flies consists of four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Here is a brief overview of each stage:
- Egg: The female mango fly lays her eggs on the soil or on objects that come into contact with the host animal. The eggs hatch within 2-3 days, depending on the temperature and humidity.
- Larva: The newly hatched larva burrows into the skin of the host animal, where it feeds on tissue fluids and grows. The larva grows rapidly and can reach up to 1 cm in length within a week.
- Pupa: After 5-8 days, the larva leaves the host animal and pupates in the soil. The pupa is protected by a hard outer shell and undergoes metamorphosis to transform into an adult fly.
- Adult: The adult mango fly emerges from the pupa after 10-14 days. The female fly then mates and lays her eggs, starting the life cycle anew.
It is important to note that mango flies do not infest humans directly, but can cause serious health problems in domestic animals, including dogs. Infected dogs may exhibit symptoms such as itching, swelling, and discharge from the affected area. Treatment typically involves removal of the larvae and proper wound care.